
Best Math Curriculum for Elementary Schools in 2026
Choosing the best math curriculum for elementary classrooms is more complex than ever.
District leaders and...
ALI Staff | Published September 22, 2021
Integrating social-emotional learning (SEL) into math instruction is more than a trend; it's a meaningful shift in how educators approach teaching and learning.
This approach not only enriches the math classroom but also equips students with essential life skills.
Let's explore how this fusion of SEL and math can redefine success for students and educators alike.

The framework of SEL is built around five core competencies:
This competency involves the ability to regulate one's emotions, thoughts, and behaviors effectively in different situations.
It includes managing stress, controlling impulses, and setting and achieving personal and academic goals.
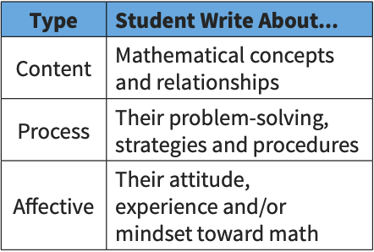
As a way to improve self-management skills among students, writing is an effective exercise.
By writing down their thoughts and ideas about math, students can express both their intellectual and emotional reactions to the subject matter.
This kind of reflection can help students better understand their level of engagement and comprehension of the lesson. Additionally, writing can help students differentiate between their feelings and behaviors.
By recognizing the space between "feeling" and "reacting," students can intentionally choose a more positive response.
The ability to manage emotions effectively can be seen in a student's level of initiative, frustration tolerance, and resilience in the face of challenges.
This refers to the ability to accurately recognize one's emotions and thoughts and their influence on behavior.
It includes assessing one's strengths and limitations and possessing a well-grounded sense of self-confidence and optimism.
Self-aware students have the ability to identify their own emotions, thoughts, and values, and how these affect their behavior.
A class activity that combines social and emotional learning (SEL) skills with mathematical concepts, such as the one described below, can assist students in developing self-awareness by paying attention to their strengths and limitations.
It also helps them keep track of what they say and how they say it. This type of exercise involves presenting a question, then asking students to create a mathematical claim that they will support.
After formulating their argument, they debate their ideas in groups, either large or small.
As students exchange ideas, they reinforce their knowledge and identify gaps in their own understanding.
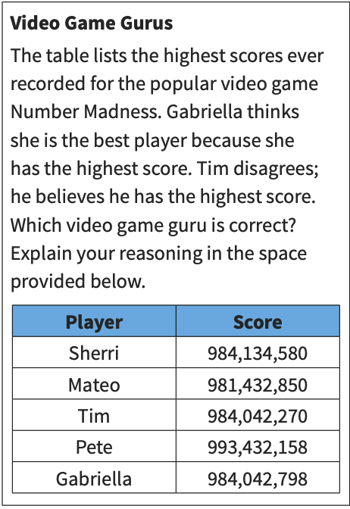
Before dividing into smaller groups, it's important to remind students that the activity is not intended to identify who is correct or incorrect.
Instead, it's an opportunity for them to discover more about themselves and develop their skills as mathematical thinkers who can respectfully express agreement or disagreement with others.
This competency involves the ability to take the perspective of and empathize with others, including those from diverse backgrounds and cultures.
It also involves understanding social and ethical norms for behavior and recognizing family, school, and community resources and supports.
This involves making constructive and respectful choices about personal behavior and social interactions based on ethical standards, safety concerns, and social norms.
The development of the core competencies mentioned in this blog leads to the ultimate objective of responsible decision-making.
Students who can effectively manage their emotions and thoughts, respect others, and communicate and collaborate well while solving problems are well-equipped to make sound decisions.
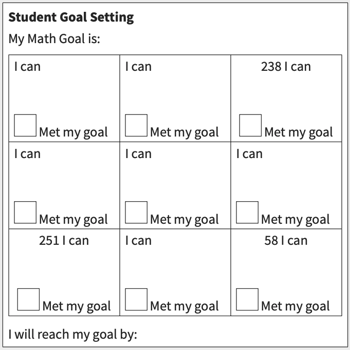
Teachers may consider using a goal sheet that provides students with a way to see the outcomes of their decisions.
Establishing personal goals helps students gain a sense of independence, and achieving those goals helps them gain a sense of self-efficacy.
This competency involves the ability to establish and maintain healthy and rewarding relationships with diverse individuals and groups. It includes effective communication, active listening, cooperation, and conflict resolution.
Social-emotional learning isn't just an extra subject; it's a key part of all learning experiences. When teachers include SEL in different subjects, students become more engaged and effective learners.
Research shows that SEL helps improve students' social behavior, lowers stress levels, and boosts academic performance. These skills are not just for the classroom; they help students in their everyday lives too.
They help students build strong friendships and make smart choices. By incorporating SEL into the curriculum, educators are preparing students to succeed in school and in life.
Developing strong interpersonal skills, such as effective communication and collaboration, is a crucial aspect of social and emotional learning.
Activities like the one below enable students to practice relationship skills while engaging in numerical reasoning.
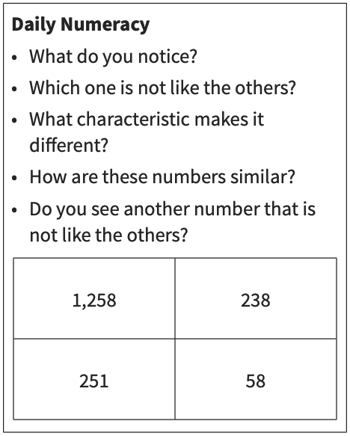
In this activity, the teacher presents a set of questions that are open-ended in nature, allowing students to observe and think before they answer.
To aid in this process, hand signals like the ones demonstrated below can be used.
These gestures can benefit introverted students by providing them with the confidence to respond while also preventing others from interrupting before everyone has had an opportunity to contribute.
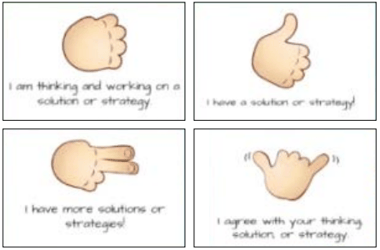
These practices can help students develop and reinforce skills such as active listening and clear communication while resisting social pressures that discourage curiosity.
It is a helpful tool that combines SEL skills with math.
In the math classroom, social-emotional learning (SEL) can be seamlessly integrated into daily instruction.
It's not just about solving equations or finding the area of a shape; it's also about developing emotional and social skills that will serve students well in all areas of life. Here are some ways SEL can be incorporated into math instruction:
Math can often present challenges that frustrate students. SEL techniques can help students learn how to cope with these challenges and embrace the productive struggle.
By teaching self-management and coping strategies, educators can help students persevere through difficult problems, enhancing both their math skills and their emotional resilience.
In many classrooms, mistakes are seen as failures. This perception is often heightened in math, a subject frequently viewed as having only one "right" answer.
This can make students more prone to feeling like failures when they make mistakes. Incorporating SEL provides the tools to change this culture, turning mistakes into learning opportunities.
Educators can create a culture where mistakes are viewed as valuable learning opportunities.
This not only boosts students' self-confidence but also encourages a growth mindset, which is crucial for mastering complex math concepts.
By reframing the role of mistakes in the learning process, SEL helps combat the fear and anxiety often associated with math, turning challenges into opportunities for growth.
Math problems can often be solved in multiple ways and SEL can encourage students to be flexible in their problem-solving approaches.
By promoting responsible decision-making and open-mindedness, educators can help students see the value in exploring different methods for solving a single problem. This in turn enriches mathematical understanding for all.
Questions are a powerful tool in the learning process. Educators can ask SEL-focused questions like, "How did it feel to solve that challenging problem?" or "What strategy can you use to tackle a similar problem in the future?"
These questions not only make students reflect on their math feelings but also on their learning processes, increasing the effectiveness of both.
SEL can be seamlessly incorporated into all parts of a lesson to create a holistic learning experience for students. Here are some examples of what a math lesson with integrated strategies and activities could look like.
Starting a lesson with SEL warmup questions or openers can set the tone for the entire class.
Questions like, "How do you feel about today's math topic?" or "What's one word to describe your feelings about math right now?" can help students become aware of their emotional states.
This not only helps in addressing math feelings but also prepares students for the lesson ahead by making them more receptive to learning.
Group activities are an excellent platform for including SEL in the math classroom.
When students work together, they naturally engage in social awareness and relationship-building.
Educators can guide this process by setting up norms for respectful discussion and problem-solving. For example, before starting a group task, the teacher might ask, "What is one thing you can do to be a good team member today?"
This fosters a more collaborative and emotionally safe math classroom.
SEL is equally, if not more, important during individual tasks. Students often face challenges when working alone, and SEL can provide them with the tools to persevere.
Teachers can encourage self-management and responsible decision-making by asking reflective questions like, "What strategy will you use to solve this problem?" or "How will you check your work?"
These questions encourage students to be mindful of their approach, thereby integrating SEL into independent work.
The conclusion of a lesson offers a valuable opportunity for both educators and students to assess academic and emotional progress.
Exit tickets can be designed to include SEL questions such as, "How do you feel about what you learned today?" or "What was challenging and how did you overcome it?"
These questions have two purposes: they measure both what students know and how they feel.
Additionally, setting aside a moment for reflection allows students to internalize their experiences, making the learning more meaningful and personal.
This reflective time can help solidify both math skills and emotional insights, offering a more comprehensive view of students' educational journey.
By incorporating SEL into each part of a math lesson, educators can create a more supportive and effective learning environment. This approach ensures that students are not just learning math but are also developing essential life skills.
Understanding the emotional landscape of the math classroom is crucial for effective teaching and learning. Below are some key points that highlight the benefits of integrating social-emotional learning (SEL) into math instruction.
The attitudes and beliefs that educators hold about math can significantly influence their students.
If teachers themselves have negative feelings towards the subject, this sentiment can easily be transferred to the students, creating a cycle of math aversion.
Incorporating SEL can help educators become more aware of their own attitudes and work on creating a more positive math learning environment.
Many students enter the math classroom already feeling insecure about their abilities.
This insecurity can be a significant barrier to learning and achievement.
SEL strategies can help students become more self-aware and manage these insecurities, thereby making the learning environment more conducive to academic success.
A growth mindset, the belief that abilities can be developed through dedication and hard work, is crucial for improvement in any subject, including math.
SEL activities can help foster this mindset by encouraging self-awareness, promoting resilience, and teaching effective goal-setting techniques.
Math anxiety is a widespread issue that affects learners of all ages. It can severely hamper performance and enjoyment in math.
SEL can offer tools to manage this anxiety, such as stress-reduction techniques and positive self-talk strategies.
By addressing the emotional aspects of learning math, SEL can help students approach the subject with more confidence and less fear.
For educators interested in diving deeper into the integration of social-emotional learning in the math classroom, here are some valuable resources.
These materials offer further insights, practical tips, and research-based methods to effectively combine SEL and math instruction.
Including social-emotional learning in math lessons offers a fuller educational experience and turns the math classroom into a place where both emotional skills and math skills grow.
For teachers, this is a chance to change what success in math looks like. Adding SEL into the mix makes the classroom a place where students learn important skills like how to bounce back from setbacks and understand others' feelings.
School leaders can help by giving teachers the tools and support they need to make these changes.
It's always a good time to start integrating SEL into your math curriculum. The benefits of combining SEL and math are too important to put off.
Let's aim to make the math classroom a place where emotional growth is just as important as learning math skills.

Choosing the best math curriculum for elementary classrooms is more complex than ever.
District leaders and...

Early childhood is perhaps the most critical moment in a student's education life.
This is the stage where a journey of...

Are students in your science classrooms merely completing activity after activity and moving on? Or do they have a...